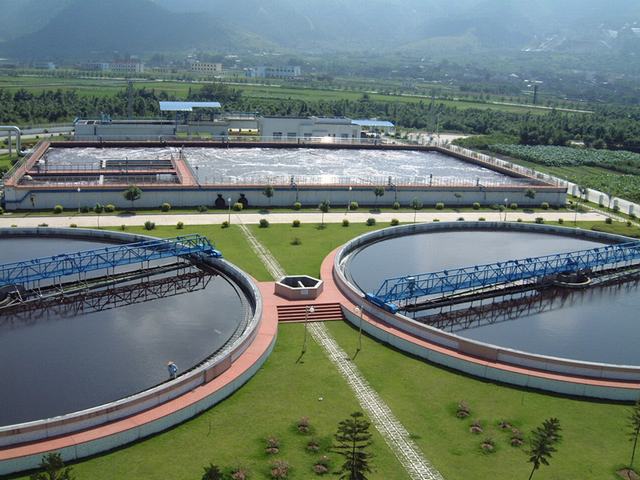
With the improvement of people’s living conditions, more and more domestic sewage has been discharged. And domestic sewage treatment process has also been continuously improved. The general process of domestic sewage treatment of our company is as follows:
In a BAF, the filler including bio-carrier & lamella is put in the treatment device to produce a large number of microorganisms through oxygen supply. The treatment device contains filter bed, aerator, water distributor, water discharge device, etc. The aerator is equipped with special-purpose aerating head to generate bubbles of small and middle size, which is then cut repeatedly by the filler to achieve the effect close to that of microporous aeration. The high concentration of sludge in the reaction tank and the compact treatment device help to reduce the floor space and the reaction time.
SPR Phosphorous Removal Process
Water eutrophication is caused by a great deal of ammonia nitrogen and phosphor in water discharged by human beings, of which phosphor is the main factor. Of all the wastewater treatment technology, Phosphorous removal technology has long been a problem in the operation of sewage treatment plants in China. Traditional physicochemical dephosphorization technology needs plenty of phosphorous removal agent, with such flaws as high operation cost and considerable sludge output; Anaerobic biological phosphorous removal process has the advantage of low operation cost, however, since it completely depends on phosphor absorption and release by microorganisms, it can hardly meet the national requirement on sewage treatment process, not to mention reclaimed water treatment.
A/O Biofilter
Chinese small-town residential areas are scattered, sewage sources are numerous, and the capacity of most urban-level sewage plants is lower than 10000 tons/day. Currently, the sewage treatment plants in large- and middle-size cities usually adopt traditional technologies including activated sludge, A2/O, SBR, and oxidation ditch. If small-town sewage treatment plants are established based on these technologies, the operation expense will be high and normal operation will not be guaranteed. Hence, according to the features of small towns, stable and reliable technologies that can help to reduce investment and operation expense and are easy to operate and manage must be used.
Treatment Process
Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal (EBPR)
Since water eutrophication in main rivers and lakes in China is serious, State Environmental Protection Administration has formulated strict discharge standards to control and alleviate phosphorous pollution. Chemical enhanced biological phosphorous removal process mainly removes organic pollutants and phosphor of all forms, integrating chemical and biological phosphorous removal: Activated sludge in the anaerobic-digested biological system generates volatile organic acid as the base material or nutrient for selective proliferation of PAOs, and then PAOs flow back to the biological system so that the biological sewage treatment system will conduct phosphorous removal efficiently; meanwhile, the phosphor produced by sludge under anaerobic condition is released and removed chemically. This high-efficient municipal sewage treatment technology meets the requirement of current stage that further phosphorous removal procedure should be performed on the base of conventional two-stage sewage treatment to solve the problem of water eutrophication.
Intermittent Cyclic Aeration
Different regions in China have very different economic development levels, and lagging-behind cities are still unable to input many money in sewage treatment. Hence, how to use limited money to reduce environmental pollution is an issue faced by many cities. Until recently, some cities still adopt first-grade or first-grade reinforced treatment technology, and effluent can not meet the requirement on organic pollutant removal specified in national second-grad discharge standard. While intermittent cyclic aeration process can meet the requirement by giving play to the high-efficiency high-load oxidation ditch and making full use of the sequencing batch reactor activated sludge process, and its cost is about 30% lower than that of second-grade biological sewage treatment system targeting organic pollutants, and thus it meets the sewage treatment requirement of current stage.
Rotary Contact Oxidation
Rotary contact oxidation process is a new generation of aerobic biological membrane technology that combines the advantage of biological contact oxidation process on the basis of biologic rotating disk. Rotary contact oxidation process and auxiliary equipment provide a simple and reliable sewage treatment method. The rotation shaft is the only rotating part in the whole treatment system, and can be repaired by ordinary technicians if it breaks down. The system biomass will be compensated automatically according to the change of organic load. The microorganisms adhering to the rotating disk is organic. When organisms in sewage increases, microorganisms will also increase; and vice versa. Thus, the work effect of the system will not be affected easily by flow rate, sudden load change, or power failure. The operation cost is low, with power consumption equal to only 1/8 to 1/3 of that of other systems. And the floor space is only half of that of conventional activated sludge system. Because the microorganisms in the system are diversified in kinds, the system can efficiently treat all kinds of industrial sewage that is difficult to be degraded.
Continuous Cycle Aeration
CCAS (Continuous Cycle Aeration System) is a continuous inflow SBR aeration system formed by improving SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor). SBR process was successfully developed in 1914, however, it is difficult to apply this process to large-scale sewage treatment plants because manual operation and management are inconvenient, monitoring method is lagged behind, and diffuser is easily clogged. SBR process was widely believed to be suitable for small-scale plants. In the 1960s, automatic control technology and monitoring technology underwent rapid development, and a new-type non-clogging microporous diffuser was developed, creating conditions for wide application of intermittent process. In 1968, the University of New South Wales in Australia and American ABJ Company jointly developed “extended aerobic activated sludge process adopting continuous inflow and cyclic discharge of intermittent reactor”. In 1986, American State Environmental Protection Bureau formally accepted CCAS as an innovative alternative technology (I/A), and now it has become the most advanced computer-controlled biological phosphorous and nitrogen removal technology.
The sewage pretreatment requirement of CCAS is not high, and only mechanical grid with a spacing of 15mm and sedimentation tank are needed. CCAS reaction tank is the core of biological treatment, in which phosphorous and nitrogen removal and degradation of organisms and suspended substance are completed, with up-to-standard effluent discharge. Pretreated sewage continuously flows into the front pre-reaction tank, in which most soluble BOD is absorbed by activated sludge microorganisms which then flow at a low speed (0.03-0.05m/min)into the reaction area through the hole in the bottom of the partition wall between main reaction region and pre-reaction region. In the main reaction region, a cycle including aeration, idle, settle and decant phases is executed to remove carbon and nitrogen through a repeated “aerobic-anoxic” process and to remove phosphor through a repeated “aerobic-anaerobic” process. The duration of each process and the running of corresponding equipment are controlled by a computer in a centralized way according to a preset and adjustable program.
SPR Treatment
In the SPR sewage treatment system, first, dissolved pollutants are separated out of simple solution by chemical method to form colloidal particles or tiny suspended particles with solid phase interface; then, organic pollutants and chroma are separated from sewage by high-efficient and economical absorbents; then, colloidal and suspended particles of all kinds are agglomerated to form large and dense flocs through microscopic physical adsorption method; and then, in the independently designed SPR high-turbidity sewage purifier, floc and water are rapidly separated based on the principle of fluid mechanics such as rotational flow and filtration hydraulics; water filtrated through the self-forming dense suspended mud layer in the tank reaches the third-grade treatment standard and can be reused; sludge in the concentration chamber is highly concentrated and discharge periodically under pressure. Since the rate of water content of sludge is low and sludge dewatering performance is good, sludge can be sent directly into mechanical dewatering device to form sludge cake which may be used to produce sideway tiles, avoiding secondary pollution.